Introduction to Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is rapidly transforming the landscape of B2B marketing by shifting from traditional, broad-based strategies to highly targeted, personalized approaches. Unlike conventional lead-generation tactics that aim to capture a large volume of prospects, ABM focuses on a select group of high-value accounts, offering tailored messaging and solutions designed to meet their specific needs. This level of personalization is delivered across multiple channels, such as email, social media, and direct outreach, ensuring that each account receives consistent, relevant communication at every touchpoint.
A key advantage of ABM is its ability to maximize return on investment (ROI) by concentrating marketing efforts on accounts most likely to convert, thereby reducing wasted resources and improving efficiency. According to studies, ABM strategies can deliver up to 87% higher ROI compared to traditional marketing approaches.
Furthermore, ABM aligns sales and marketing teams, enabling them to collaborate on shared goals. This alignment streamlines communication, shortens the sales cycle, and improves the overall customer experience by ensuring that marketing efforts seamlessly transition into sales activities. As a result, businesses using ABM are better positioned to build long-lasting relationships with key decision-makers, driving both customer retention and long-term revenue growth.
Why ABM is More Effective Than Traditional Lead-Based Marketing
Traditional lead-based marketing strategies cast a wide net, aiming to capture as many prospects as possible and nurturing them through the sales funnel. However, many of these leads may never convert, resulting in wasted resources and lower ROI. In contrast, Account-Based Marketing (ABM) focuses on fewer, high-value accounts that are more likely to generate significant revenue. This targeted approach allows businesses to tailor personalized marketing campaigns for each account, addressing their specific pain points, needs, and goals.
By honing in on a select group of high-revenue clients, ABM delivers more relevant and personalized messaging, which in turn drives better engagement and higher conversion rates. This personalized engagement builds stronger relationships between businesses and their key accounts, fostering trust and loyalty that traditional marketing often struggles to achieve.
Additionally, ABM enables closer collaboration between sales and marketing teams, aligning them around the same goals and accounts, ensuring a seamless customer experience from marketing outreach to closing the deal. Traditional marketing often lacks this alignment, leading to disjointed efforts and lower success rates. Overall, ABM’s focus on quality over quantity makes it a more effective strategy for driving long-term growth in B2B businesses.
What is ABM?
Account-Based Marketing is a strategic approach in which marketing and sales teams collaborate to create personalized buying experiences for a select group of high-value accounts. Unlike traditional B2B marketing strategies that cast a wide net, ABM focuses on specific accounts and tailors marketing efforts to meet the unique needs of those businesses.
This targeted method means companies can prioritize accounts based on factors such as industry, revenue potential, and the likelihood of converting. The goal is to treat each account as a market of one, ensuring personalized campaigns that resonate more deeply with decision-makers.
Key Components of ABM
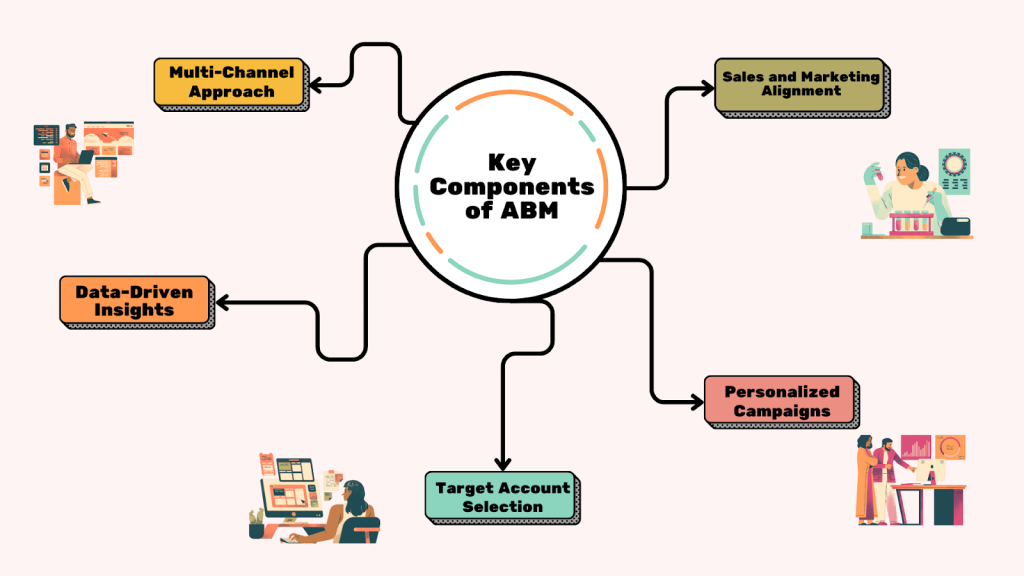
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) relies on several critical components to drive success. From aligning sales and marketing teams to identifying high-value target accounts, each element plays a vital role in creating personalized campaigns that resonate with decision-makers. Understanding these components is essential for executing a successful ABM strategy that scales and delivers a higher return on investment (ROI). Let’s explore these key elements in detail and how they contribute to ABM’s effectiveness in the B2B landscape.
1. Sales and Marketing Alignment
A fundamental element of successful ABM is the alignment between sales and marketing teams. “In a traditional marketing approach, the sales and marketing departments often work in silos, which can lead to disjointed strategies and inefficiencies. However, ABM demands close collaboration between these two departments. By aligning goals, resources, and strategies, both teams can work cohesively towards nurturing and closing high-value accounts,” explains Arvind Rongala, CEO of Edstellar. Sales teams benefit from marketing’s detailed research and insights on each target account, while marketing can tailor campaigns based on direct feedback from sales.
For example, both teams must agree on the target accounts, the messaging, and the roles each team will play in moving the accounts through the buying journey. In doing so, businesses ensure that their marketing efforts are directly tied to sales outcomes, making the overall strategy more efficient and goal-oriented.
2. Target Account Selection
Selecting the right accounts is the cornerstone of an effective ABM strategy. Unlike broader B2B marketing efforts that target a wide range of prospects, “ABM focuses on a smaller number of high-value accounts that have been identified based on specific criteria. These criteria typically include factors like industry, revenue potential, business needs, and alignment with the company’s ideal customer profile (ICP),” explains Tal Holtzer, CEO of VPS Server.
Account selection involves deep research and data analysis to identify which businesses are the best fit for your offering. For example, a technology solutions provider might prioritize targeting companies within the financial services sector that have large IT budgets and a demonstrated need for cybersecurity solutions. Once these high-value accounts are identified, businesses can allocate resources to create personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with the specific pain points and goals of each account.
3. Personalized Campaigns
One of the key differentiators of ABM is the level of personalization involved in each campaign. “Instead of using generic messaging, ABM campaigns are tailored to address the unique needs, challenges, and opportunities of each target account. This could include personalized emails, customized content, bespoke product demonstrations, or targeted ads designed specifically for decision-makers within those accounts,” says Scott Trachtenberg, CEO of ADA Site Compliance
For instance, if you are targeting a healthcare company, your marketing efforts might focus on how your product or service can help streamline patient data management while complying with industry regulations. Similarly, if you are targeting a manufacturing company, the messaging might highlight your solution’s ability to enhance supply chain efficiency. Personalization helps build trust and credibility, positioning your company as a valuable partner rather than just another vendor.
4. Data-Driven Insights
Data and analytics play a crucial role in the success of any ABM initiative. “The use of CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and account insight tools enables businesses to track engagement, identify trends, and optimize campaigns based on real-time data,” explains Jeffrey Zhou, CEO and Founder of Fig Loans. These tools help marketers better understand the needs and behaviors of each target account, allowing them to make informed decisions about how to engage with key stakeholders.
For example, data might show that a particular account is highly engaged with your content but hasn’t yet converted. Armed with this insight, your sales team can follow up with a more personalized offer or demo that addresses the account’s specific concerns. This level of insight not only improves engagement but also helps to shorten the sales cycle by delivering relevant information at the right time.
5. Multi-Channel Approach
ABM isn’t limited to a single platform or marketing channel. Instead, it involves a multi-channel approach to ensure that your target accounts are engaged across multiple touchpoints, including email, social media, paid ads, webinars, and more. The goal is to create a cohesive and consistent experience for the target account, regardless of where or how they interact with your brand.
For instance, a campaign might start with personalized emails that direct the target account to a customized landing page, followed by retargeting ads on social media platforms like LinkedIn. This multi-channel approach ensures that your message reaches the account through various avenues, increasing the chances of engagement and conversion.
How ABM Helps Scale B2B Businesses
1. Focused Resource Allocation
“ABM allows businesses to allocate resources more efficiently. Instead of wasting time and money on low-potential leads, companies can concentrate their efforts on accounts with a higher probability of converting,” explains Sandra Malouf, President of Eurolog Packing Group. By focusing on high-value accounts, businesses see a better return on investment (ROI). Studies show that ABM can deliver up to 87% higher ROI compared to traditional marketing methods.
2. Enhanced Personalization
“One of the most significant benefits of ABM is the level of personalization it enables. By crafting tailored content, product demonstrations, and solutions, companies can address the specific pain points and challenges of their target accounts. This personalized approach fosters stronger relationships with decision-makers and improves the chances of closing deals,” explains Sai Blackbyrn, CEO of Coach Foundation
For instance, a marketing campaign targeting a healthcare organization may focus on how a solution streamlines patient data management while ensuring regulatory compliance. This level of customization resonates with the healthcare organization’s specific concerns, making the marketing efforts far more effective.
3. Better Sales and Marketing Alignment
One of the key challenges in many organizations is the disconnect between sales and marketing teams. ABM bridges this gap by aligning both departments around shared goals and target accounts. According to a recent study, businesses with strong sales and marketing alignment achieve 19% faster revenue growth and 15% higher profitability.
ABM ensures that both sales and marketing are on the same page, working together to create a seamless customer experience from the initial marketing outreach to the final sale. This collaboration improves lead quality, shortens the sales cycle, and boosts conversion rates.
4. Measurable ROI and Scalability
ABM strategies are highly data-driven, allowing businesses to track the performance of each campaign and optimize future efforts based on these insights. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as account engagement, deal size, and revenue growth provide clear metrics for measuring success. Companies that implement ABM strategies often see larger deal sizes and higher customer lifetime value due to their focus on high-potential accounts.
ABM is also highly scalable. As a business grows, ABM efforts can be expanded to target additional high-value accounts or even entire industry verticals. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt their strategies as they scale without sacrificing the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns.
The Role of Technology in Powering ABM Success
Technology is the backbone of any successful Account-Based Marketing (ABM) strategy, enabling businesses to deliver personalized experiences at scale. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms like Salesforce and HubSpot are essential for tracking account interactions, storing valuable data, and ensuring consistent communication across teams. These tools allow businesses to keep detailed records of account behavior, preferences, and engagement, ensuring that each touchpoint is relevant and timely.
In addition to CRMs, marketing automation platforms like Marketo streamline the execution of multi-channel campaigns. Automation helps businesses manage email marketing, targeted ads, and content distribution, all while ensuring that messaging is tailored to the unique needs of each account.
Data analytics further enhances ABM by providing insights into account-level performance and engagement. This data helps marketing and sales teams refine their outreach, ensuring that the right message reaches the right decision-maker at the right time. Together, these technologies empower businesses to create more targeted, effective ABM campaigns, driving higher engagement and ROI.
Leveraging Content Marketing for ABM
Content marketing is essential in ABM strategies, as it enables businesses to engage decision-makers with highly relevant, personalized materials. Unlike broad-based campaigns, ABM content is tailored to address the specific challenges and goals of target accounts. This can include personalized emails, case studies, webinars, and account-specific proposals designed to resonate with key stakeholders.
Each piece of content must align with the different stages of the buyer’s journey whether it’s awareness, consideration, or decision-making. By providing valuable, customized insights at every stage, businesses can build stronger relationships and drive conversions.
Personalization at Scale: How to Strike the Right Balance
Scaling ABM without losing the personalized touch is a key challenge for B2B businesses. As organizations target more accounts, maintaining the level of customization that makes ABM effective becomes difficult. To strike the right balance, businesses can leverage marketing automation tools and CRM platforms to manage outreach while still delivering personalized content.
By segmenting accounts based on shared characteristics such as industry, company size, or common pain points, businesses can create semi-personalized campaigns that retain relevance without requiring a fully custom approach for each account. This combination of high-touch engagement and scalability allows businesses to expand their ABM efforts without sacrificing the personal connection that drives results.
Types of Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Businesses can adopt different ABM strategies depending on their objectives, account types, and available resources. These strategies typically fall into three categories: One-to-One, One-to-Few, and One-to-Many ABM.
1. One-to-One ABM
One-to-One ABM is the most personalized and resource-intensive type of ABM. It focuses on creating bespoke marketing campaigns for individual, high-value accounts. This strategy is often used when targeting large enterprises that represent significant revenue potential. In this model, the marketing and sales teams work closely to tailor all communications, content, and outreach specifically to one account. Every detail is customized, from personalized content to account-specific offers and solutions. Given the high degree of personalization involved, One-to-One ABM is ideal for long-term, high-revenue relationships where the lifetime value of the account justifies the investment. This method is especially effective in industries where long sales cycles and complex buying processes are common, such as enterprise software or large-scale manufacturing. However, because of the substantial resources and time required, One-to-One ABM is often reserved for a select few accounts that offer the highest revenue potential or strategic significance.
2. One-to-Few ABM
One-to-Few ABM, sometimes referred to as “cluster-based” ABM, targets a small group of accounts that share similar characteristics, such as industry, company size, or specific challenges. Instead of creating highly personalized campaigns for each individual account, marketing efforts are semi-customized to address the needs and pain points of the group as a whole. This allows businesses to scale their ABM efforts more efficiently while still providing a level of personalization that resonates with the target accounts.
For example, a SaaS company might group several healthcare organizations together and create tailored messaging around data security and compliance—topics that would be relevant to all businesses within the healthcare sector. While this approach lacks the hyper-personalization of One-to-One ABM, it still delivers targeted content and solutions that are more effective than broad, generalized marketing efforts. One-to-Few ABM is often used when businesses want to expand their ABM reach but still maintain a focus on high-value or strategically important accounts.
3. One-to-Many ABM
One-to-Many ABM is the most scalable form of ABM and is used to target a broader range of accounts. While it involves less personalization compared to the other two types, One-to-Many ABM still focuses on tailoring messages to specific segments. This approach is supported by marketing automation tools and CRM systems, which allow businesses to run large-scale campaigns across multiple accounts while maintaining relevance through segmentation.
In this model, businesses use data and insights to group accounts by shared attributes such as company size, industry, or business challenges, and then run automated campaigns that deliver customized content to each segment. For instance, a B2B company selling cloud solutions might target all mid-sized financial institutions with a campaign focused on improving operational efficiency. Although One-to-Many ABM is less personalized than One-to-One or One-to-Few approaches, it allows businesses to reach a larger number of accounts while still delivering content that speaks to their specific needs.
This strategy works well for businesses looking to scale their ABM initiatives without incurring the high costs associated with deep personalization. It also provides a way to nurture and engage with accounts that may not yet be ready for the intensive focus of a One-to-One or One-to-Few strategy, but still have potential for future growth.
ABM’s Role in Customer Retention and Expansion

Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is not only effective for acquiring new customers but also plays a pivotal role in retaining and expanding existing accounts. By continuously nurturing relationships with current clients, businesses can leverage ABM to identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities, offering tailored solutions that meet evolving business needs. For instance, if a client’s priorities shift, ABM strategies can be adapted to present new products or services that address those changes, thus enhancing customer loyalty.
Additionally, ABM helps prevent customer churn by providing personalized engagement and ensuring that clients feel valued through consistent communication and solutions that are specific to their challenges. By focusing on the long-term growth of key accounts, ABM fosters stronger partnerships, making it easier for businesses to expand their offerings and maximize the customer lifetime value. This strategy ultimately leads to more sustainable growth through deepened client relationships.
Challenges in Implementing ABM
While Account-Based Marketing (ABM) offers significant benefits, its implementation comes with several challenges that businesses must navigate to ensure success.
1. High Initial Investment
One of the main challenges of ABM is the substantial upfront investment required. Unlike traditional marketing strategies, ABM is resource-intensive, demanding advanced tools, technologies, and personnel. Businesses often need to invest in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, marketing automation platforms, and analytics tools to effectively manage accounts, track engagement, and optimize campaigns. Additionally, crafting highly personalized content for each target account requires dedicated time and expertise, leading to higher costs in content creation and campaign execution. For smaller businesses, this investment can be a significant barrier.
2. Organizational Alignment
Successful ABM requires close alignment between sales, marketing, and other key departments such as customer success and IT. Ensuring that all teams work together towards shared goals, target accounts, and messaging is crucial for creating a seamless customer experience. However, achieving this alignment can be difficult, especially in organizations where departments operate in silos. Without strong leadership buy-in and a collaborative culture, miscommunication can derail ABM efforts.
3. Data Management and Accuracy
ABM is heavily data-driven, relying on detailed insights about target accounts to create personalized strategies. However, obtaining and maintaining accurate data can be a challenge. Businesses must invest in data enrichment tools to ensure they are targeting the right accounts and engaging them with relevant content. Additionally, outdated or inaccurate data can lead to wasted resources, targeting accounts that may no longer be viable or missing key decision-makers.
4. Measuring Success
Measuring the success of ABM campaigns can also be complex. Unlike traditional lead-based marketing, ABM focuses on long-term relationship building and revenue growth from specific accounts, making traditional metrics such as lead volume less relevant. Instead, businesses need to track more nuanced KPIs such as account engagement, deal velocity, and revenue attributed to specific accounts. However, setting up the right metrics and aligning them with business objectives can be challenging, especially for businesses new to ABM.
5. Scaling Personalized Efforts
As businesses grow, scaling ABM efforts becomes a challenge. While ABM can be highly effective for targeting a small number of high-value accounts, expanding this approach to a broader range of accounts without losing personalization is difficult. Businesses must find ways to leverage automation while still maintaining the level of customization that makes ABM successful. This balance between scalability and personalization is often tricky to manage, requiring the right mix of technology and human touch.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, the right tools, and a commitment to collaboration across teams. However, for businesses that invest in the process, the long-term benefits of ABM such as strong customer relationships, higher ROI, and sustainable growth make it a critical strategy in the B2B space.
Measuring the Long-Term Impact of ABM
The success of Account-Based Marketing (ABM) goes beyond short-term metrics like lead generation. To truly measure the long-term impact, businesses need to focus on account engagement over time, deal velocity, customer lifetime value (CLV), and sales pipeline influence. These metrics offer insights into the depth of relationships built with high-value accounts and the efficiency of converting those relationships into revenue.
Tools like CRM platforms and marketing automation systems can track account activity across multiple touchpoints, helping businesses monitor engagement levels and refine campaigns. Metrics such as account engagement score, which aggregates data from emails, social media, and website interactions, give an indication of how involved target accounts are.
Refining key performance indicators (KPIs) over time is essential for ongoing campaign improvement. Businesses should continuously analyze which strategies yield the highest ROI, adjust outreach methods, and personalize messaging to keep accounts engaged throughout their lifecycle, ensuring long-term success.
Conclusion
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is a powerful strategy for scaling B2B businesses, focusing on personalized marketing efforts for high-value accounts. By targeting specific accounts and aligning sales and marketing teams, ABM delivers more effective results than traditional broad-based marketing approaches. The collaboration between these teams helps shorten sales cycles, increase deal sizes, and enhance customer retention. ABM allows businesses to focus their resources on accounts with the highest potential, improving return on investment (ROI). For instance, companies implementing ABM strategies have seen up to 87% higher ROI compared to other marketing methods.
While ABM can require significant investment in technology, resources, and collaboration, its scalability makes it suitable for businesses of all sizes. As companies grow, ABM efforts can expand to include more accounts or entire industry segments. With the right tools, such as CRM systems and data analytics, ABM strategies can evolve alongside business growth.
In the future, as marketing technology advances, the personalized experiences that ABM offers will become even more accessible, making it a crucial strategy for B2B companies aiming to drive sustainable growth in a competitive landscape

Andrej Fedek is the creator and the one-person owner of two blogs: InterCool Studio and CareersMomentum. As an experienced marketer, he is driven by turning leads into customers with White Hat SEO techniques. Besides being a boss, he is a real team player with a great sense of equality.
